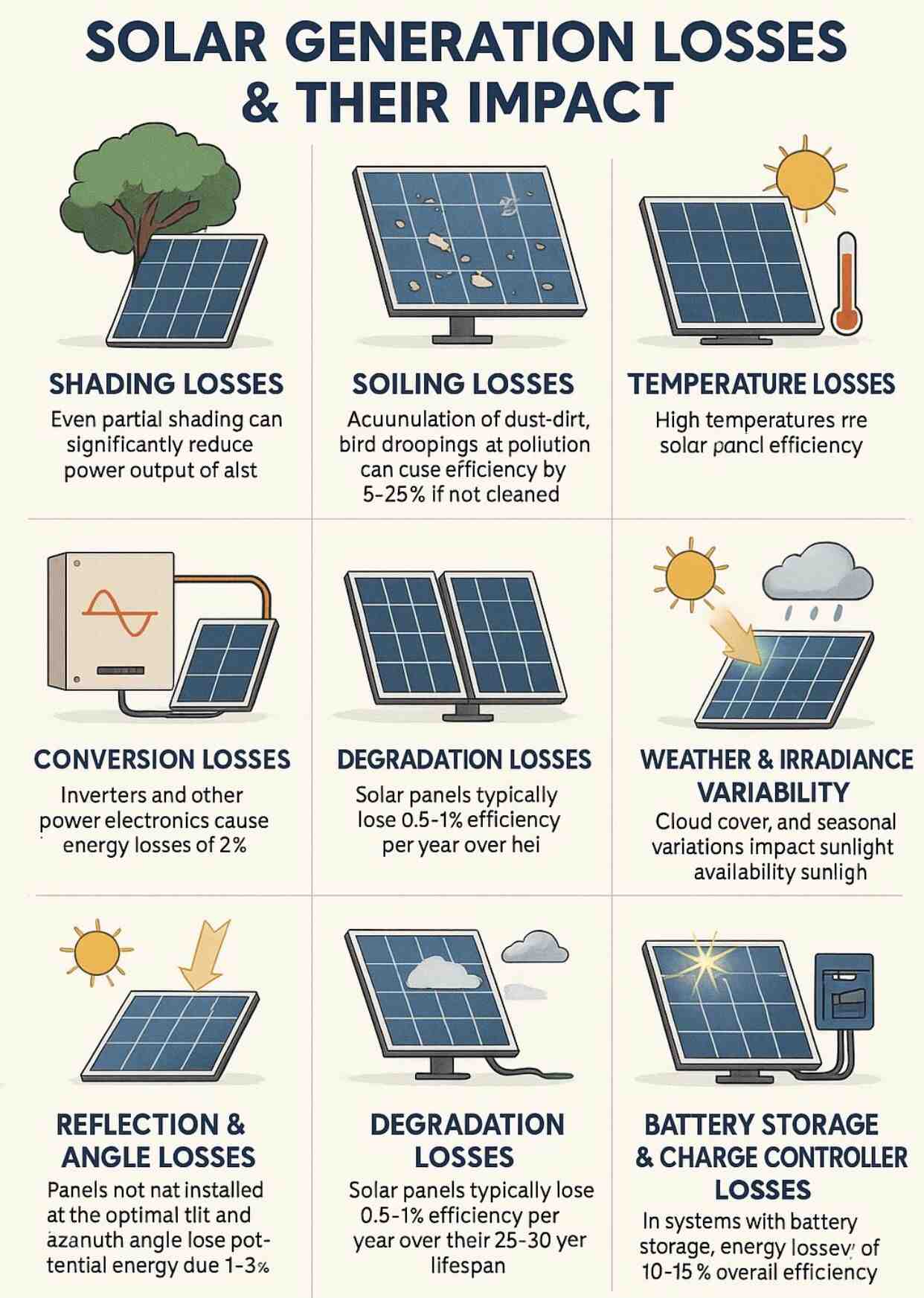
Solar energy systems are subject to various types of that can significantly impact overall power generation efficiency. Understanding these losses is crucial for optimizing system performance and maximizing returns.
1️⃣ Shading Losses
Even partial shading from nearby trees, buildings, or debris can drastically reduce the power output of a solar panel. Since panels are often connected in series, shading of a single panel can affect the performance of the entire string.
2️⃣ Soiling Losses
Accumulation of dust, dirt, bird droppings, and pollution on solar panels blocks sunlight, reducing efficiency by 5–25% if not cleaned regularly. Routine maintenance is vital to mitigate soiling effects.
3️⃣ Temperature Losses
Solar panel efficiency decreases as temperature rises. For every 1°C increase above the standard test condition temperature of 25°C, panel output drops by approximately 0.3–0.5%, depending on the panel technology used.
4️⃣ Mismatch Losses
Manufacturing differences, aging, and varying degradation rates cause performance inconsistencies between panels, leading to mismatch losses and reduced overall system output.
5️⃣ Conversion Losses
Inverters and other power electronics are responsible for converting DC power generated by panels into AC power for use. This conversion process typically results in 2–5% energy losses, with older or lower-quality inverters potentially causing even higher losses.
6️⃣ Cable & Transmission Losses
As electricity flows through cables, some energy is lost as heat. Poor cable sizing, inferior materials, and long transmission distances can cause losses ranging from 1–3%.
7️⃣ Degradation Losses
Over time, solar panels naturally degrade, typically losing around 0.5–1% of their efficiency per year. This gradual reduction results in lower energy generation over a 25–30 year panel lifespan.
8️⃣ Weather & Irradiance Variability
Changes in weather conditions, such as cloud cover, fog, and seasonal shifts, impact the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels. These variations cause fluctuations in daily and seasonal power generation.
9️⃣ Reflection & Angle Losses
Incorrect installation angles or lack of anti-reflective coatings can cause panels to reflect sunlight instead of absorbing it, leading to 1–3% energy losses. Proper orientation and tilt optimization are critical for maximizing sunlight absorption.
🔟 Battery Storage & Charge Controller Losses
In solar systems with energy storage, losses occur during the charging and discharging processes, as well as through power conversion. These losses can account for 10–15% of the energy, reducing the overall efficiency of the system.
Typical Total Losses (W/o Storage):
~20–35% (depending on system quality, location, and maintenance)
Typical Total Losses (With Storage):
~30–45% (due to additional battery-related losses)