HJT solar cells have attracted widespread attention due to their high energy conversion efficiency, fewer manufacturing steps, lower preparation temperature and better temperature coefficient. The low-temperature preparation characteristics of HJT solar cells limit the choice of paste, resulting in poor conductivity of silver paste and high cost. In order to reduce costs, the industry has developed a variety of solutions, such as silver-coated copper paste, electroplating copper technology, laser transfer technology and busbar-free technology.
Preparation of solar cells
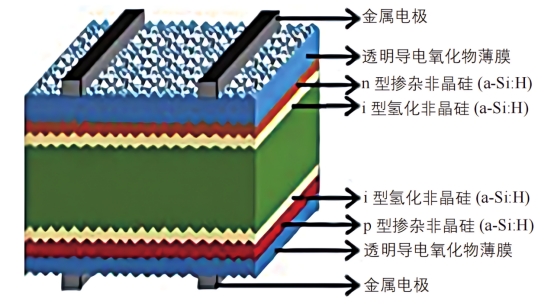
Schematic diagram of the structure of HJT solar cells
Using n-type silicon wafers as substrates, HJT solar cells are prepared by alkali texturing, plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) to prepare amorphous silicon thin films, magnetron sputtering (PVD) to deposit transparent conductive oxide thin films (TCO), and screen printing to make metal electrodes. Silver-coated copper paste with a silver content of 50% is used to prepare metal electrodes.
Structural characterization and tensile properties of silver-coated copper grid lines
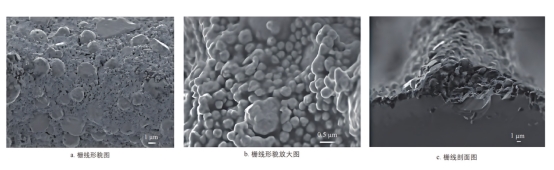
SEM image of the fine grid lines on the front of the silver-coated copper HJT solar cell
The powder in the silver-coated copper paste is spherical and well dispersed. The grid lines show a clear structure, and the silver-coated copper particles are evenly distributed in the grid lines, indicating that the paste can form good conductivity during low-temperature sintering. This uniform distribution helps to improve the conductivity of the electrode and the contact performance with the transparent conductive oxide (TCO) film.

The morphology of the front grid line of the silver-coated copper HJT solar cell
The grid line morphology image taken by a 3D microscope shows the flatness and uniformity of the grid line. There are differences in the flatness of the grid line, and the ups and downs are uneven, which may be due to the poor uniformity of the line shape caused by the mesh knot of the screen.
The average line width of the silver-coated copper grid line is about 43µm, the average line height is about 14µm, and the aspect ratio is about 32.5%, which is slightly lower than the performance of the conventional low-temperature silver paste HJT solar cell grid line, but the silver-coated copper grid line can still achieve good electrode function and has sufficient mechanical strength.
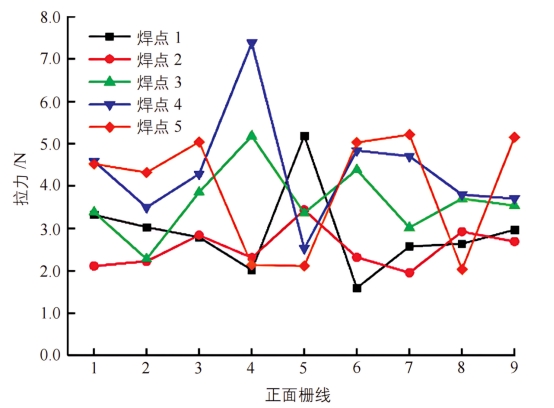
Silver-clad copper HJT solar cell front grid line tensile force diagram
The tensile force test results of the front grid line of the silver-clad copper HJT solar cell: the tensile force is basically above 2.0 N, the highest reaches 7.4 N, and the average tensile force is 3.5 N, indicating that the mechanical properties of the grid line are qualified.
The tensile performance of the silver-clad copper grid line is equivalent to that of the traditional low-temperature silver paste, or even slightly higher, indicating that its mechanical properties can meet the actual application requirements.
Electrical performance research
Distribution of photoelectric conversion efficiency of silver-clad copper HJT solar cells
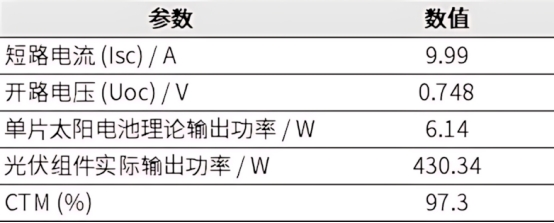 Electrical performance of silver-coated copper HJT solar cells
Electrical performance of silver-coated copper HJT solar cells
The photoelectric conversion efficiency of silver-coated copper HJT solar cells is mainly concentrated between 24.3% and 24.7%, with the highest proportion being 24.5% (accounting for 22.8%), indicating that silver-coated copper HJT solar cells have good photoelectric conversion performance. The photovoltaic module prepared with 72 silver-coated copper HJT solar cells has a packaging loss (CTM) of 97.3%, which is comparable to conventional low-temperature silver paste HJT photovoltaic modules.
Reliability testing
Initial performance testing
 Initial performance parameters of 5 silver-coated copper HJT photovoltaic module samples. The average output power of the samples is 434.49 W on the front and 365.33 W on the back, and the bifacial power generation efficiency reaches 84.1%.
Initial performance parameters of 5 silver-coated copper HJT photovoltaic module samples. The average output power of the samples is 434.49 W on the front and 365.33 W on the back, and the bifacial power generation efficiency reaches 84.1%.
DH test
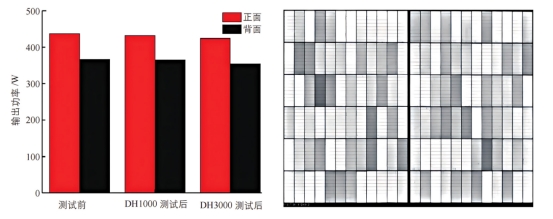
Output power attenuation and EL image of samples after DH test
Low power attenuation: After 3000 hours of damp heat test, the output power attenuation rate of the module is only 2.6%, showing good stability.
No internal defects: No cracks or black spots were found in the EL image, indicating that the internal structure of the module is intact and the silver-clad copper grid has excellent anti-oxidation performance in a damp and hot environment.
Reliability verification: The silver-clad copper HJT photovoltaic module performs well under damp and hot conditions, verifying its long-term reliability in complex environments and providing strong support for the practical application of silver-clad copper slurry.
"DH1000+load" test
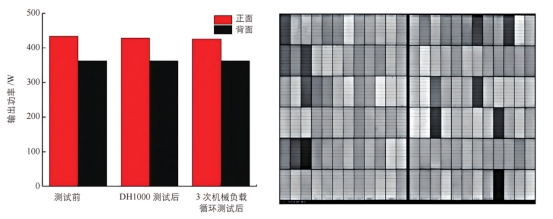
Output power attenuation and EL image after the "DH1000+mechanical load" test
Low power attenuation: The output power attenuation on the front side is only 0.68%, and the output power on the back side increases slightly, indicating that the module can still maintain high performance under complex environmental conditions.
No internal damage: No abnormalities were found in the EL image, further verifying the integrity and damage resistance of the silver-clad copper grid under mechanical load.
Reliability verification: The silver-clad copper HJT photovoltaic module performs well under damp heat and mechanical load conditions, verifying its long-term stability and reliability in practical applications.
TC test
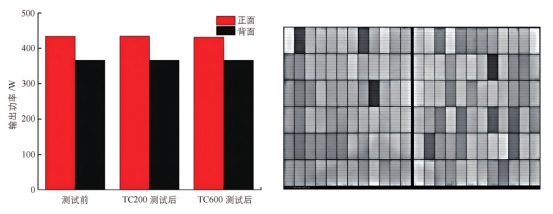
Output power attenuation and EL image of samples after TC test
Low power attenuation: After 600 temperature cycles, the output power attenuation rate of the front side is only 0.72%, and the output power attenuation rate of the back side is only 0.03%, showing the good durability of the module under temperature change environment.
No internal damage: No cracks, black spots or other abnormal phenomena were found in the EL image, further verifying the internal structural integrity of the module after the temperature cycle test.
Reliability verification: Silver-clad copper HJT photovoltaic modules perform well under temperature cycle conditions, verifying their long-term stability and reliability in complex environments.
PID test
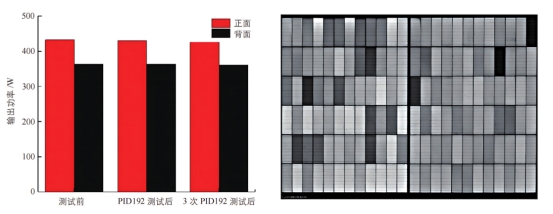
Output power attenuation and EL image of samples after PID test
Low power attenuation: After 3 PID tests for a total of 576 hours, the output power attenuation rate of the front side was only 1.09%, and the output power attenuation rate of the back side was only 0.63%, showing the good stability of the module under potential induced conditions.
No internal damage: No cracks, black spots or other abnormalities were found in the EL image, further verifying the internal structural integrity of the module after the PID test.
Reliability verification: Silver-clad copper HJT photovoltaic modules performed well in the PID test, verifying their long-term stability and reliability in high voltage and humid environments.
Silver-clad copper HJT solar cell cost analysis
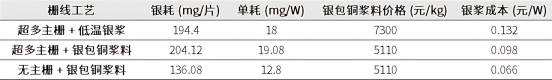
The cost forecast analysis of silver-coated copper paste compares the cost of silver-coated copper paste under different processes, including super-busbar + low-temperature silver paste, super-busbar + silver-coated copper paste and no busbar + silver-coated copper paste. The use of silver-coated copper paste can reduce the cost of silver paste by about 25.8%, and the cost can be further reduced by 50% in combination with no busbar technology.
Through the application research of silver-coated copper paste with a silver content of 50% in HJT solar cells, the structure and tensile properties of silver-coated copper grid lines, the electrical properties of solar cells and the reliability of photovoltaic modules are comprehensively analyzed. The HJT solar cells prepared with silver-coated copper paste have excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency of 24.37%, which is comparable to the performance of conventional low-temperature silver paste photovoltaic modules. In addition, the silver-coated copper HJT photovoltaic modules performed well in reliability tests such as damp heat test (DH), thermal cycle test (TC) and potential induced decay test (PID), and the output power attenuation rate was less than 3%, further verifying its stability and reliability in harsh environments.