
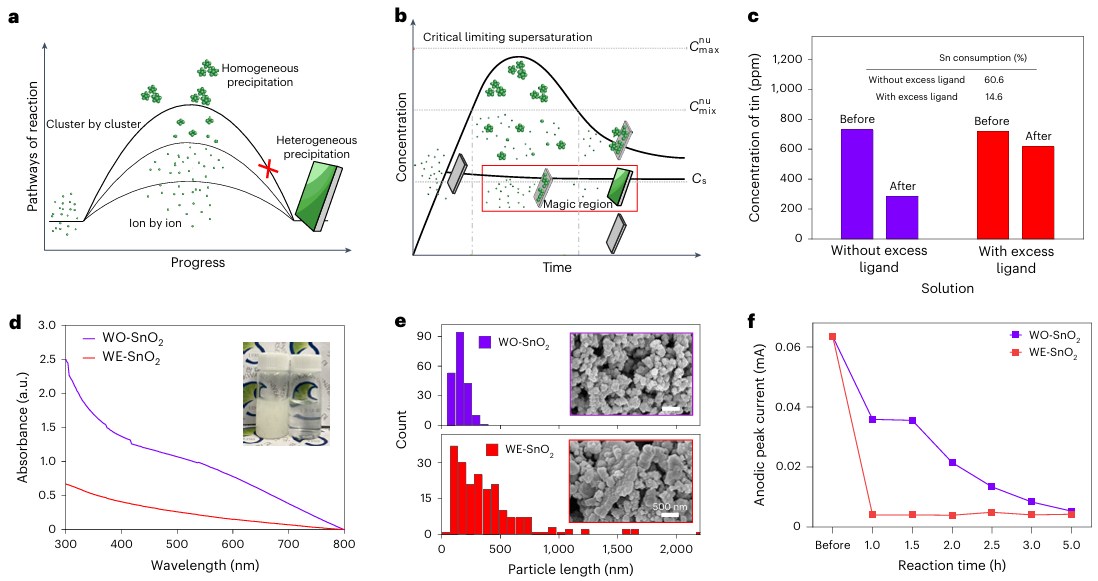
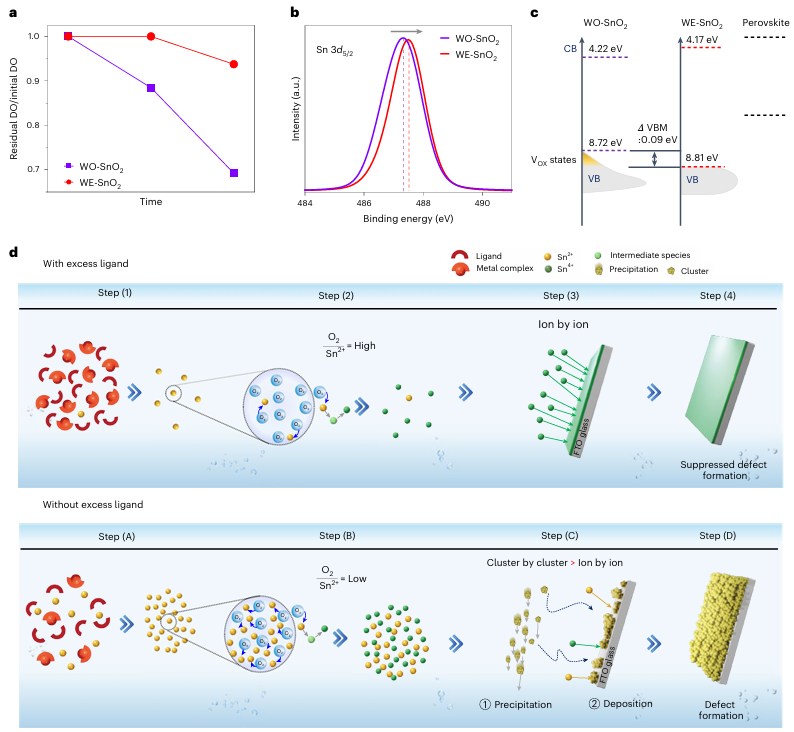
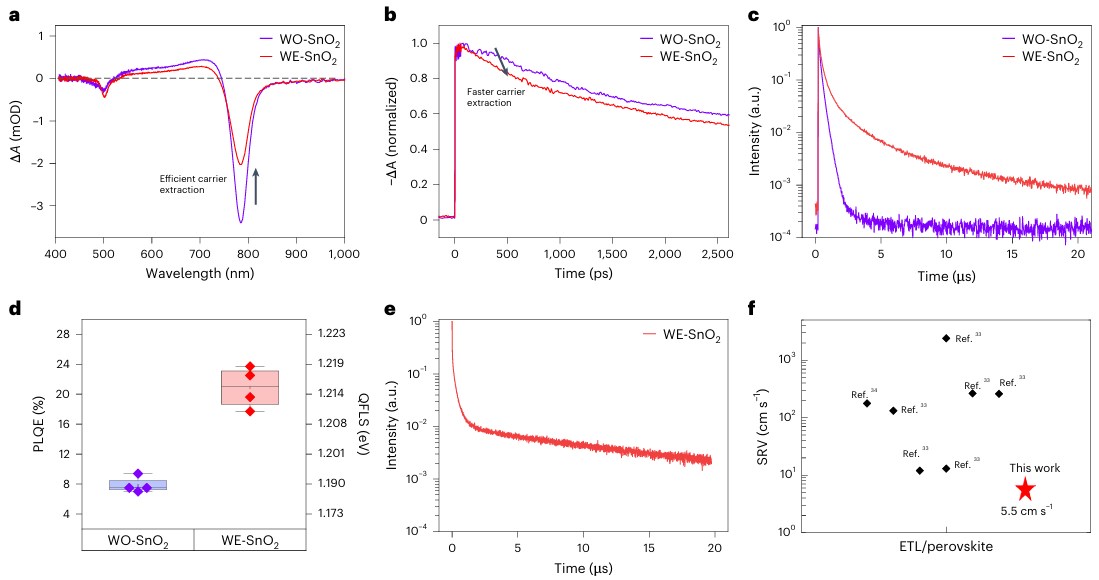
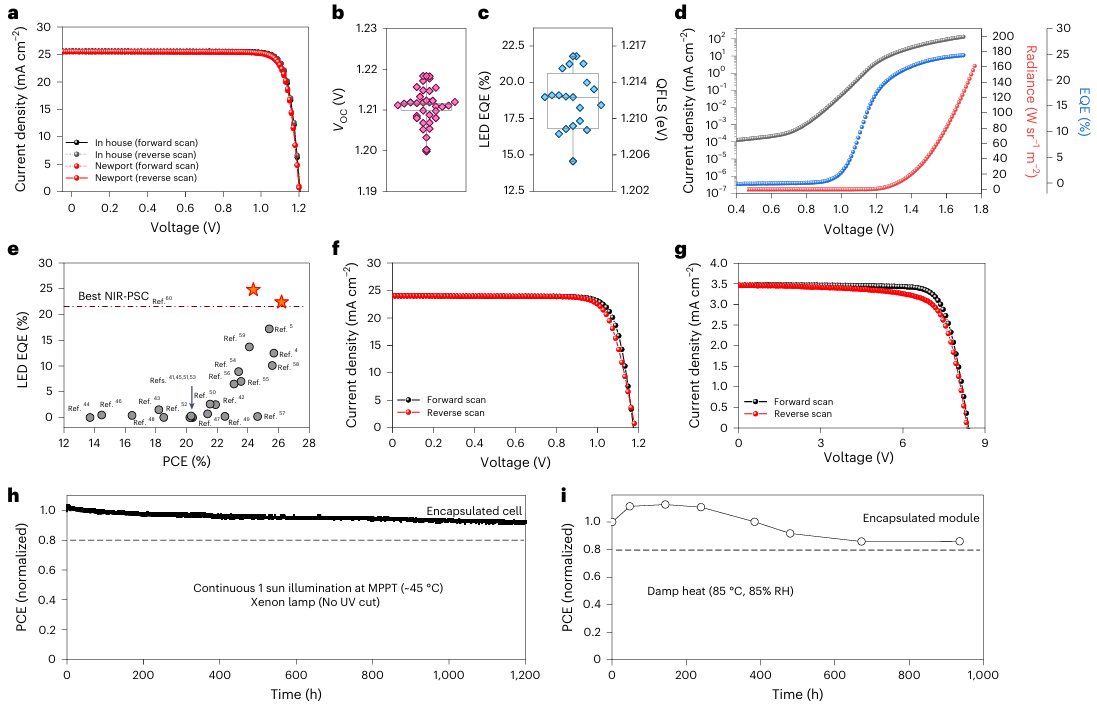
 The efficiency of perovskite solar cells can be improved by depositing electron transport layers using chemical bath deposition (CBD). However, the conventional CBD method takes time to obtain uniform films on large substrates, and often fails to deposit high-quality films due to incomplete surface coverage and oxidation. In view of this, on June 4, 2025, Seong Sik Shin of Sungkyunkwan University & Sang Il Seok of UNIST published a study in Nature Energy on suppressing defects in SnO2 through an excess ligand strategy to achieve efficient light-emitting perovskite solar cells, demonstrating an excess ligand strategy based on tin dioxide (SnO2) CBD, which suppresses cluster-by-cluster paths while promoting ion-by-ion paths to create uniform films. This method enables the rapid synthesis of high-quality SnO2 electron transport layers and reduces defect density. The resulting SnO2 film exhibited excellent optoelectronic properties, including a low surface recombination velocity (5.5 cm/s) and a high electroluminescence efficiency of 24.8%. These improvements enabled perovskite solar cells to achieve energy conversion efficiencies as high as 26.4%, perovskite modules to achieve 23%, and carbon-based perovskite cells to achieve 23.1%. This highlights its potential for low-cost, large-scale production of high-efficiency solar devices.
The efficiency of perovskite solar cells can be improved by depositing electron transport layers using chemical bath deposition (CBD). However, the conventional CBD method takes time to obtain uniform films on large substrates, and often fails to deposit high-quality films due to incomplete surface coverage and oxidation. In view of this, on June 4, 2025, Seong Sik Shin of Sungkyunkwan University & Sang Il Seok of UNIST published a study in Nature Energy on suppressing defects in SnO2 through an excess ligand strategy to achieve efficient light-emitting perovskite solar cells, demonstrating an excess ligand strategy based on tin dioxide (SnO2) CBD, which suppresses cluster-by-cluster paths while promoting ion-by-ion paths to create uniform films. This method enables the rapid synthesis of high-quality SnO2 electron transport layers and reduces defect density. The resulting SnO2 film exhibited excellent optoelectronic properties, including a low surface recombination velocity (5.5 cm/s) and a high electroluminescence efficiency of 24.8%. These improvements enabled perovskite solar cells to achieve energy conversion efficiencies as high as 26.4%, perovskite modules to achieve 23%, and carbon-based perovskite cells to achieve 23.1%. This highlights its potential for low-cost, large-scale production of high-efficiency solar devices.
Original article:
htthttps://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-025-01781-1